
Difference Between Active Power & Reactive Power TheElectricalGuy in 2023 Power, Active
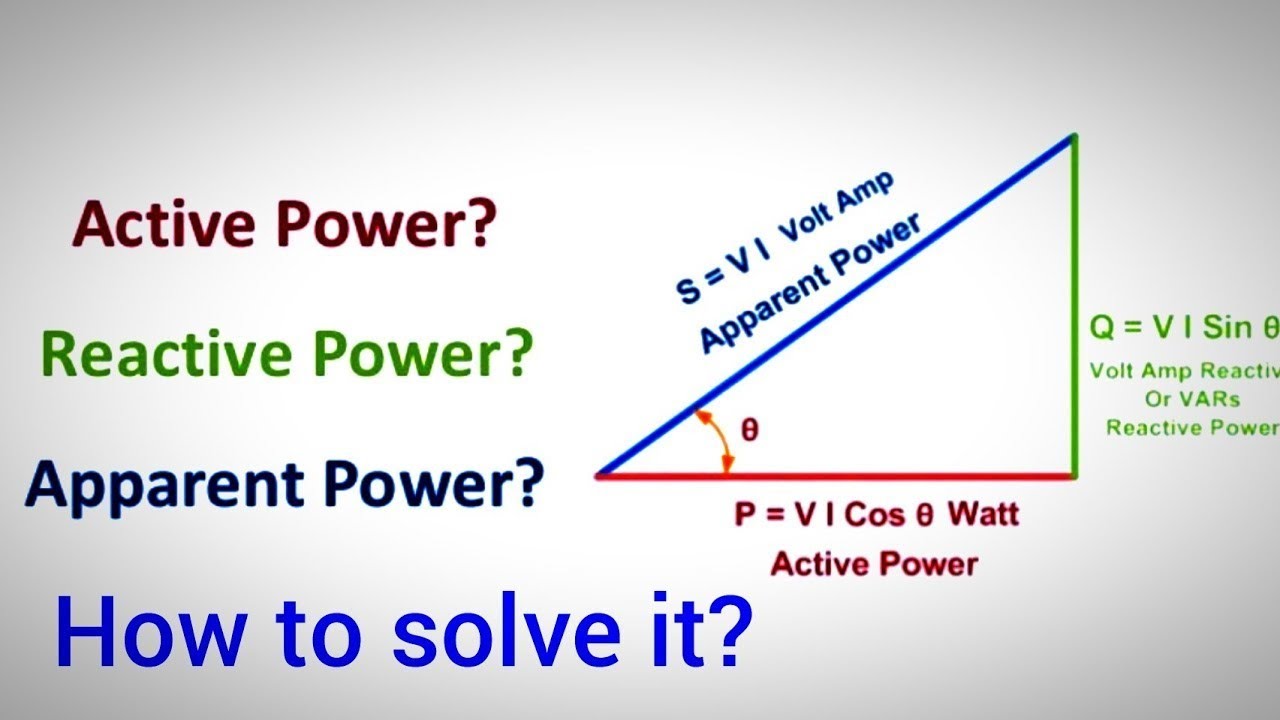
The active, apparent and real power induces in the circuit only when their current lags behind the applied voltage by an angle of Φ. The right-angled triangle shown below shows the relation between the active, reactive and apparent power. Where, S - apparent power Q - reactive power P - Active power. Content: Active Vs Reactive Power

Active and reactive power variations of the synchronous motor for case... Download Scientific
As a rule, true power is a function of a circuit's dissipative elements, usually resistances (R). Reactive power is a function of a circuit's reactance (X). Apparent power is a function of a circuit's total impedance (Z). Since we're dealing with scalar quantities for power calculation, any complex starting quantities such as voltage.
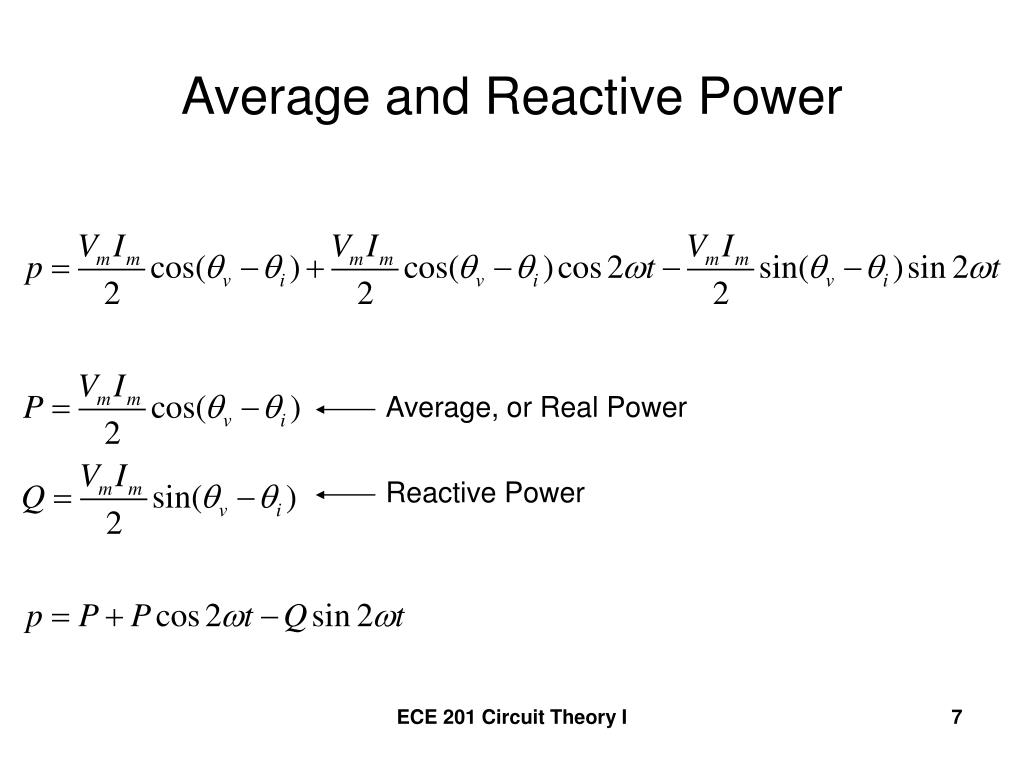
PPT Instantaneous Power PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2688644
Active power is the real power electrical devices consume to perform useful work. Reactive power is the imaginary power that helps maintain the voltage in the electrical system. Both active and reactive power are essential for proper functioning electrical systems, but only active power contributes to energy consumption.

Main Difference Between Active and Reactive Power YouTube
Beer Analogy of Active power, Reactive power, Apparent Power and Power factor Role of Active Power and Reactive Power. There is an important relationship between active and reactive power and the post below will help to understand that why active power (P) is called true power and reactive power (Q) is called imaginary power.
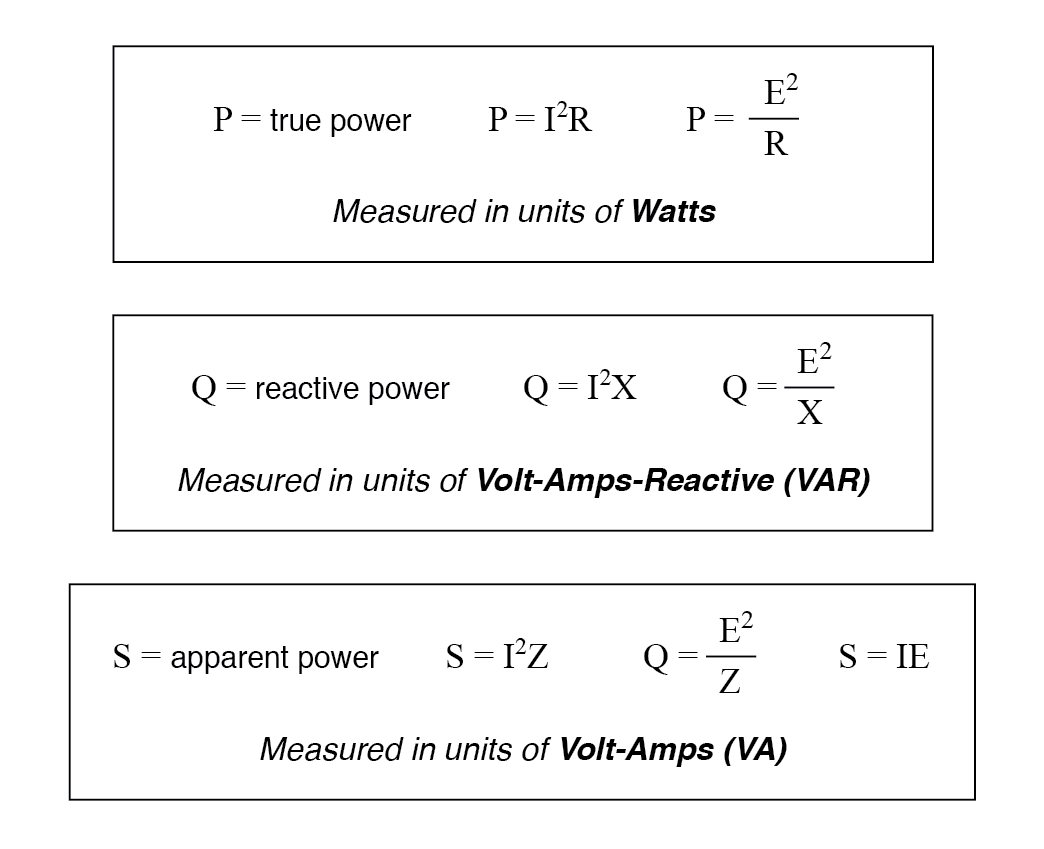
Equations For Power In A Circuit
Active power can be measured by inserting a wattmeter into the circuit. To calculate the reactive power, the formula for calculating the reactive power (Q) can be used: Reactive power (Q) = √ (S^2 - P^2), with: Q: Reactive power in volt-amperes-reactive (VAR). S: Apparent power in volt-amperes (VA).

Active vs Reactive vs Apparent Power Learn the Differences
Characteristics: Active Power: Reactive Power: Definition: The True or Real or Actual Power dissipated in the circuit is known as Active Power which is actually utilized or consumed. (Also known as useful or watt-full power). A Power which continuously bounces back and forth between source and load is known as Reactive Power. (Also known as useless or watt-less Power).

Apparent, active, and reactive power (PQS)
Electrical power consumed by a resistance in an AC circuit is different to the power consumed by a reactance as reactances do not dissipate energy. In a DC circuit, the power consumed is simply the product of the DC voltage times the DC current, given in watts. However, for AC circuits with reactive components we have to calculate the consumed.

Difference Between kWh (Active Energy) and kVAh (Reactive Energy) Billing
Active vs. Reactive Power: Comparison Chart. Summary Active vs Reactive Power. In AC circuits, active power is the real power consumed by the equipment to do useful work meaning the power dissipated by a load, whereas reactive power is an imaginary power which is not used directly for work. Instead it bounces back and forth continuously which.
HOW TO CALCULATE ACTIVE POWER REACTIVE POWER AND APPARENT POWER BY OM MODERN ACADEMY
Apparent power, measured in volt-amperes (VA), is the combination of active and reactive power. It represents the total power drawn by a load and is the product of voltage and current in an AC circuit. Apparent power can be calculated using the formula S = VI, where V is voltage and I is current. In a right-angled triangle, with active power as.

Active and Reactive Power Control of Synchronous Machine YouTube
The required power supply to an electric circuit depends on the. active power - real electrical resistance power consumption in circuit; reactive power - imaginary inductive and capacitive power consumption in circuit; The required power supply is called the apparent power and is a complex value that can be expressed in a Pythagorean triangle relationship as indicated in the figure below.
What is reactive power and active power? testblog2
The combination of Active Power and Reactive Power is known as Apparent Power. It is the total power of the circuit. Mathematically Apparent power is defined as the product of the root mean square (RMS) value of voltage and current irrespective of its phase angle. It is denoted by the English alphabet 'S' and It is measured in kVA, MVA.

Difference Between Active & Reactive Power The Engineering Knowledge
The glass filled with cocktail represents the true power and the frothy foam on the top is reactive power and the sum of active and reactive is apparent power in the system. Figure 2. A famous analogy to describe active, reactive, and apparent power . Active Power or Real Power. Active power is often called real, actual, true, or useful power.

Active vs Reactive vs Apparent Power Learn the Differences
Reactive power is the power, in VAR or kVAR, stored and released by inductors and capacitors. Reactive power is returned to the source without being consumed. However, current flows through the circuit to supply the reactive power. Wires, components, and devices must be sized to allow for the increased current flow from the reactive power.

Understanding the basics of reactive power
Real power is the power actually consumed due to the resistive load and apparent power is the power the grid must be able to withstand. The unit of real power is watt while apparent power unit is VA (Volt Ampere) Real, reactive and apparent power comparison. A famous analogy is made with the glass of beer and the froth of the beer.

What do apparent power, real power, instantaneous power and reactive power all mean in AC
Active power or Real power. Active power is the actual power dissipated or consumed by an electric load. It depends on the total load impedance. Active power is also known as True power and Real power. It is measured in Watts. Active power is denoted by the letter P. Active power does not produce any phase shift between current and voltage.

Active, Apparent and Reactive Power in the Power Triangle. Basic concepts of Electrical
The relationship between these three types of power is described by the Pythagorean theorem. Mathematically, it's represented as S² = P² + Q², emphasizing that the apparent power (S) is the square root of the sum of the squares of active power (P) and reactive power (Q). Understanding apparent, active, and reactive power provides a.
- John De Bever En Kees
- Call Of Duty Mw3 Ds
- Welke Insecten Kun Je Eten
- Holiday Inn Express Singapore Orchard Road
- Hoeveel Renners In De Tour 2023
- Au Pair Willem Frederik Hermans
- Heb Je Voor Albanie Een Paspoort Nodig
- Wie Heeft Wie Is De Mol Bedacht
- Welke Paddenstoelen Kun Je Eten
- Amsterdam Cape Town Flight Time